Juniper Publishers- Open Access Journal of Case Studies
Advances in Therapeutics of Celiac Disease
Authored by Anantha Naik Nagappa*
Abstract
The celiac diseases are on the rise with an incidence of 1:100. The celiac disease is caused by the activation of an immune system to the gluten found in staple food like wheat, rye and barley. In this disease ninety percentage of the patients get remission of the disease, when the patients are fed with gluten free diet. However, ten percentages of the patients don't respond to gluten-free diet. These patients are classified Refractory Celiac Disease (RCD) and (Non-Refractory Celiac Disease) NRCD. Some of these patients were going to develop the cancer of the colon called as Enteropathy-Associated T-Cell Lymphoma (EATL). There is no treatment for RRCD, NRCD and EATL. The advances in the treatment for RCD, NRCD and EATL include new strategy using monoclonal antibiotics and other Biotherapeutics approaches. These advances are discussed in these reviews.
Keywords: Celiac disease; Gluten; Refractory Celiac Disease; Non-celiac Gluten Sensitivity
Introduction
Celiac diseases (CD) are induced by gluten and related proteins which are like to cause intestinal damage. The major intervention of CD is avoided of gluten rich diet, which usually results improvement in lesions. However, all CD patients don't respond to clinical or histological recovery such patients are called Non- responsive CD. They have continued symptoms of lethargy, abdominal pain and diarrhea. Investigation of NRCD in the literature indicates there are no definitive treatments or management of NRCD patients. However, an arbitrary period of 6-12 months gluten free diet has been suggested. However, the NRCD patients don't show any improvement in the severity of the histological improvement or clinical symptoms. Hence, it is very clear the CD patients don’t respond positively with a designated as NRCD. Practical management depends upon the cause of persistent symptoms. Other kind of CD called Refractory Celiac disease, which are distant Non response to GFD [1]. RCD is defined by symptomatic and persistent villous atrophy despite of strict GFD. It has further divided into Type 1and Type 2. The clinical monitory has revealed the 80% of the RCD patient’s posses the intra epithelia lymphocytes which are easily recognized in the intestinal mucosal (CD 103+, intracellular CD3+, CD4", CD8", surface CD3"). These have originated by monoclonal T-cell receptors gamma gamma-gene arrangements which are detectable PCR analysis of biopsy specimen of intestinal of CD patients. The presence of aberrant has been termed as Type-1 RCD, which is usually not present in type1 RCD. It is interesting to know that the RCD-II patients have the greater mortality than RCD I. The major cause of death is attributed to the development of enteropathy associated with Enteropathy-associated T- cell lymphoma (EATL). The EATL is known to be malignant and it is hypothesized the presence of RCD T-cell phenotype represent a cryptic T-cell lymphoma. Patients with NRCD and RCD are usually present with weight loss, malabsorption and diarrhea [2].
Epidemiology
Its prevalence worldwide fluctuates around 0.5-1% of the population. An increase in frequency has been reported in the last years, doubling its prevalence in the last 20 years. Environmental factors have been proposed to explain this phenomenon, such as increased wheat consumption and infections at the beginning of life, although the evidence is not yet conclusive. According to the 2010 national health survey, a prevalence of between 0.6 and 0.8% is estimated in Children. The wheat usage has increased due to introduction of new recipes like pizza, Burger and bakery products which is the main ingredient of above junk food is divide of fibers present in whole grain flour. The refined white flour containing more gluten and less fiber helps the deposition of gluten in the large intestine. If instead whole grain wheat flour is there then it will help by facilitating the bowl evacuation and also these fibers are metabolized by the bacteria to Prebiotics in all such mechanism helps in the maintains of large intestine health and minimizing the gluten toxicity [3,4].
The Role of Gluten
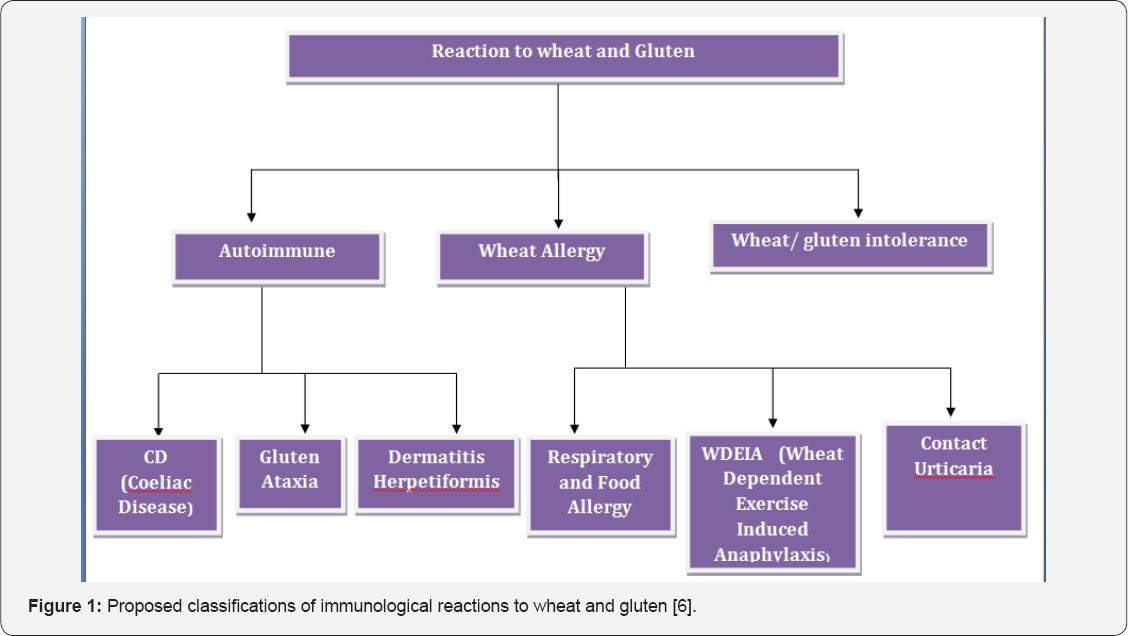
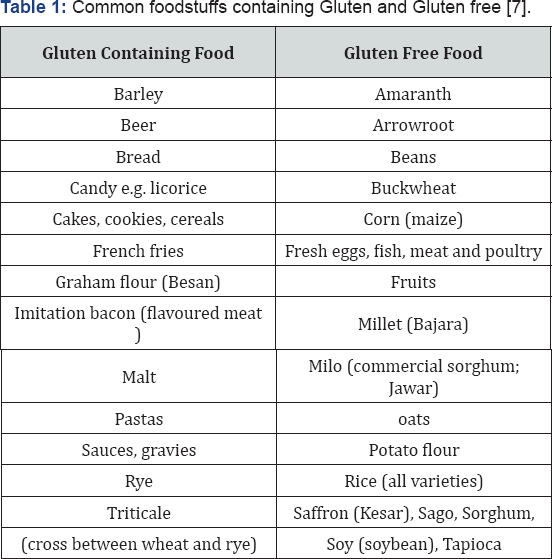
The gluten is present in cereals like white, barley and rye which are cultivated in the Mediterranean countries and North America. Among these wheat is most popular staple food. It is used for making breads like roti and chapatti. In India, wheat was introduced by USA who gave the wheat in times of major famine. The gluten is a protein which contains extensive glutamine and proline. Gluten is poorly digested in the small intestine. The undigested gluten gets lodged in the large intestine where it is deposited. The deposited gluten is partially digested by the bacteria's leading to formation of toxic substance which has gliadin. Gliadin is a peptide alcohol-soluble fraction. The complex metabolites enter the lamina propria of the large intestine. After passing the lamina propria they are recognized by immune surveillance as foreign antigens and thus initiate immune response. These peptides pass through the epithelial barrier of the intestine, possibly during intestinal infections or when there is an increase in intestinal permeability, and interact with antigen-presenting cells in the lamina propria. Undigested molecules of gliadin, such as a peptide from an a-gliadin fraction made up of 33 amino acids, are resistant to degradation by gastric, pancreatic, and intestinal brush-border membrane proteases in the human intestine and they remain in the intestinal lumen after gluten ingestion which constantly keeping the immune response [5]. See Figure 1 [6] and Table 1 [7] for proposed classifications of immunological reactions to wheat and gluten and common foodstuffs containing Gluten and Gluten free respectively.
Pathogenesis
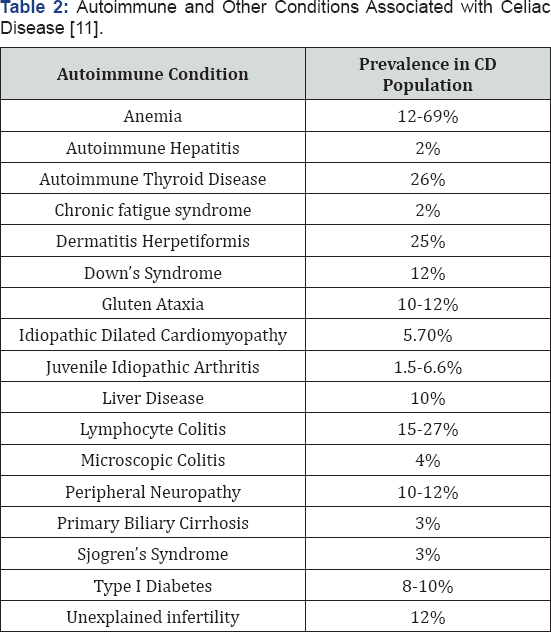
A complex interplay between genetic, environmental and immunological factors plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of CD. In the 1940s Dicke identified gluten as the environmental trigger of CD. Gluten is a heterogeneous protein whose toxic fractions are a mixture of alcohol-soluble proteins called gliadins, which are found in cereals such as wheat, barley, rye consumed in most countries [5]. Gut enzymes are not capable of digesting gliadin fractions. Large proline/glutamine peptides therefore accumulate in the small intestinal lumen and may lead to pathological innate and adaptive immune responses in genetically predisposed subjects. CD is serious autoimmune disorder that usually occurs in genetically predispose persons, in response to continued exposure gluten rich diet it is estimated to report 1 in 100 worldwide. Clinically it is difficult to diagnose because it affects the patients in diverse manner for example, there are more than 200 types of celiac disease which may either in manifest symptoms in digestive system or some other part of the body. It is also interesting to know the CD may also develop in children or adults. Unfortunately some of the patients are symptoms they may show up negative results but a positive intestinal biopsy. However, CD are at a risk of long term complication despite they have the symptoms or symptomless. Digestive tract symptoms in children's include abdominal bloating and pain, chronic diarrhea, vomiting, constipation, pale, foul-smelling, weight loss, fatigue, irritability and behavioral issues, dental enamel defects of the permanent teeth, delayed growth, short stature, failure to thrive, and Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. In adults, celiac disease patients having the less digestive symptoms like in children's however it is observed that 1/3 of celiac patients may experience. The adult celiac patients suffer from the iron deficiency anemia have fatigue, bone or joint pain, osteoporosis or osteopenia (bone less), liver and biliary tract disorder (transsminitis, fatty liver, primary sclerosing cholangitis) depression or anxiety, peripheral neuropathy (tingling, numbness or pain in the hands and feet) irregular menstrual cycle, canker sores inside the oral cavity, dermatitis, herpitiformis (itchy skin rashes). As per the World gastroenterology the celiac disease are classified into Classical celiac disease and non classical celiac disease. The CCD patients have malabsorption, diarrhea, steatorrhea (pale foul fatty stoles) and weight loss and growth failure among children’s. A non classical CD the patients may have mild GIT symptoms without clear signs of malabsorption. They may show up the abdominal distention with pain and symptoms like iron deficiency of anemia, fatigue, peripheral neuropathy unexplained elevated liver enzymes, reduced bone mass with frequent fractures, and folic acid vitamin B12 deficiency. They may also show late monarchy and late menopause unexplained infertility. They have dental enamel defects and suffer from depression and anxiety with dermatitis. There are also some patients who remained asymptomatic are called as patients which silent celiac disease. They don't have any symptoms but suffer from villous atrophy in small intestine. There is a genetic connection observed in first degree relatives or CD patients [8-10]. See Table 2 [11] for autoimmune conditions associated with CD.
Enteropathy-Associated T-Cell Lymphoma (EATL) [5]
The cancer of the small intestine develops in celiac patients usually at the age of sixty and above. The disease is usually associated with Enteropathy the hallmark of T-cell lymphoma. The patients show up symptoms of Enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma occurs in adults, with the incidence peaking in the sixth decade of life, and is usually at an advanced stage at diagnosis. Symptoms may include malaise, anorexia, weight loss, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and unexplained fever and night sweating. The symptoms indicate the sensitivity to gluten challenge when patients are fed on GFD. There will be an improvement in the patient condition indicating that the celiac disease which is presented responsive to the gluten sensitization. However, the disease has been gone further too Enteropathy- associated T-cell lymphoma (EATL). This condition is malignant in nature needs proper diagnosis and treatment with appropriate chemotherapy and radiation therapy. It is agreed Enteropathy- associated T-cell lymphoma is complication of celiac disease. This disease rise from the intraepithelial T-lymphocytes which go into transformation due to poor adherence to GFD, HLA-DQ2 homozygosity and late diagnosis of CD. The suspicion of EATL is lead to extensive diagnostic efforts with magnetic resonance entroclysis, positron emission tomography scan, and histological identifications lesion. The treatment high dose of chemotherapy followed by the surgical resection along with autologous stem cell transplantation. However, strict adherence to GFD can only be the best prevention of exhilaration of EATL.
Refractory Celiac Disease (RCD)
Refractory Celiac Disease is a form of CD that not responds histological to at least one year of a strict GFD. It is also observed it is also involved in patients who initially response of GFD but gradually become non response. RCD further classified into RCDI and RCDII. RCD I is characterized by persisting atrophy of the villous even when patient is on strict GFD. Phenotypically normal intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELS). Whereas, in RCD II a clonally expansion of abnormal intraepithelial lymphocytes lacking surface CD3, CD8 and T-cell receptor markers with expression of intracellular CD3. This condition frequently evolves into EATL is the most serious complications of CD [5,12].
Non-celiac Gluten Sensitivity (NCGS)
People with Non-celiac Gluten Sensitivity (NCGS) experience symptoms similar to CD. These symptoms get resolved when they are on strict GFD. It is suspected the triggering of systemic immune response is not only due to gluten but also other antigenic substances which are present in the wheat and other cereals. Apart from the gluten and other antigenic components there seems to partially undigested carbohydrates which can sensitize the CD symptoms. These patients who become responsive to gluten, wheat free diet may fail to respond due to acquired sensitivity to the undigested carbohydrate. There are new approaches and scientific endures to understand the distinct pathology, and identification of biomarkers along with development in therapeutic Non-celiac Gluten Sensitivity diseases [7].
Diagnosis
Due large variety of celiac disease exceeding two hundred. It is extremely difficult to diagnose the type of celiac disease. The Biopsy, serological tests and histopathological are the standard tests. The objective of diagnosis of CD is to estimate whether villous atrophy has begin or what extent villous atrophy has spread across. The histology aims at identifying any cancerous transformation is there. The serology is to assess the immune responsiveness of the celiac diseases [13].
Treatment
The treatment of the celiac disease logically seems to be the withdrawal of gluten, wheat and other food which the patients sensitive. The pathological consequience of the CD involves disturbed microbiota leading to severe deficiency of B complex vitamins folic acid, B12, fat-soluble vitamins, iron, and calcium, . Hence, it is a necessary to assess the nutrition status of the patients. All patients with celiac disease should undergo screening for osteoporosis, which has a high prevalence in this population. It become necessary to administer total parental nutrition as patient's intestine is unable to absorb the nutritional factors due to atrophy of the villous. The health care team should include a skilled dietitian who monitors the patient's nutritional status and dietary adherence on a regular basis. In children, ongoing evaluation includes monitoring of growth and development [3,5,8,14].
Conclusion
The celiac diseases which are non responding to gluten free diet is a disease for which no definitive treatment although these patients make ten percentage of celiac disease. They are important because these patients are different from the patients who are responding to gluten free diet. The responses for the gluten free diet are measured by histopathological evidence freedom symptoms of celiac disease and improvement in index of quality of life. The RCD, NRCD and EATL in which the atrophy of the villous paralysis the absorptive capacity of the small intestine. There are severe deficiency of nutritious factors which can lead to malnutrition and calcium deficiency leads to osteoporosis. As these patients are unable to absorb through oral route. It becomes important to build and sustain the nutritional status by total parental nutrition many CD patients are frequently admitted to orthopedic ward for treatment of fractures of bone. Hence, there is need for a skilled dietician. The EATL is a cancer of small intestine it is recommended with chemotherapy. The treatment high dose of chemotherapy followed by the surgical resection along with autologous stem cell transplantation.
For more articles in Open Access Journal of Case Studies please click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/jojcs/index.php



No comments:
Post a Comment