Juniper Publishers- Open Access Journal of Case Studies
Tuberculosis of Wrist Joint in Young Female: A Very Rare Case
Authored by Vinil Shinde
Abstract
Tuberculosis (TB) is major public health issue globally especially in developing countries like India. Though pulmonary TB is common the extra pulmonary TB is also on the rise. Tuberculosis of wrist especially in younger population is very rarely reported. We have discussed a very rare of case of tuberculosis of wrist joint in young female patient.
Introduction
Tuberculosis (TB) is major public health issue globally especially in developing countries like India. There has been a significant worldwide increase in the prevalence of tuberculosis (TB) and of its extrapulmonary manifestations. Osteoarticular TB accounts for 1-2% of all the TB cases in the western world [1].
We rarely encounter Tuberculosis of the wrist joint that to in young patients. It is very important to suspect Tuberculosis as probable diagnosis in presence of non-specific clinical signs and symptoms. We have discussed a very rare of case of tuberculosis of wrist joint in young female patient.
Case Report
History
13 years old female patient came with complain of pain and swelling over left wrist since 3 weeks. There was history of trivial trauma to left wrist joint 3 weeks back. For the same patient consulted a general practitioner and took symptomatic treatment for the same. She was given tablets details of the same were not available with the patient or parents of the patients. Pain persisted and swelling increased in size over the period. There was no history of fever but there was little weight loss.
Local Examination
On local examination of Left Wrist joint at our hospital we observed swelling over the dorsum of the left wrist joint. There was local rise of the temperature. Tenderness over the left wrist joint was also observed. The wrist joint was fluctuant. Dorsiflexion was 15 degrees and palmar flexion was 20 degrees.
Investigations
Complete Blood Count showed increase in WBC count to 16000 per microliter. On further investigation erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) was increased to 46 and C-reactive protein (CRP) was increased to 36.
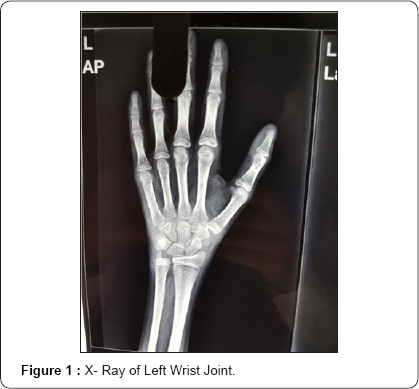
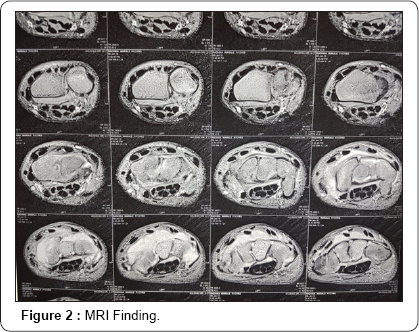
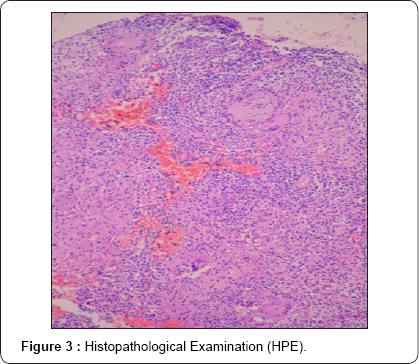
X ray done elsewhere showed no bony abnormality. While repeat X-ray showed periosteal reaction near distal region of ulna. MRI findings showed Heterogenous enhancement of all carpal bones with marrow edema. There was moderate joint effusion/soft tissue thickening showing patchy restricted diffusion post contrast enhancement. Fluid life signal along flexor and extensor tendons was also observed and there was Osteonecrosis/sclerosis of Capitate. Sample sent for culture showed mycobacterium complex grown after two weeks incubation.
Management
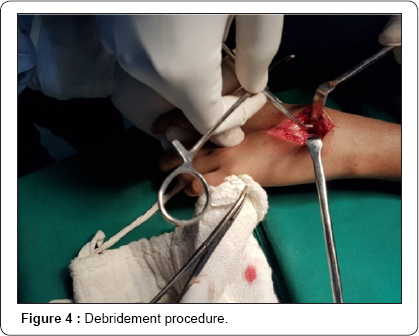
Patient was posted for debridement. Dorsal approach to the wrist was taken. Tendons of EDI & EDC were retracted. Joint capsule was incised. Synovial sample collected. Semi solid caseous purulent material identified and removed. Joint cavity was thoroughly debrided. Wash was given and wound was closed. Patient currently started on anti tubercular treatment as per recommended schedule and patient is symptomatically feeling better (Figure 1-4).
Discussion
Tuberculosis infection of the musculoskeletal system is rare even in areas of high TB prevalence [2]. Hand and wrist involvement are seen in only 10% of patients with musculoskeletal disease [3]. The symptoms initially are nonspecific in the form of joint pain, swelling, effusion, stiffness, carpal tunnel syndrome, limitation of movement, and discharging sinuses. Constitutional symptoms include low-grade fever, night sweats, weight loss, and anorexia. Blood tests may show mildly raised or even normal inflammatory markers [4].
Karthigesu M et al. [5] have reported a rare case of tuberculosis of wrist joint in elderly (70 year old) lady. They concluded that it is always safer to have high index of suspicious in treating elderly patients as they usually present with atypical presentation comparing to younger patients. The timely treatment of tuberculosis, will improves the general condition and reduces the morbidity [5].
Patel YC et al. [7] reported a rare case of tuberculosis of wrist joint in 24 year old male patient presented with progressive left wrist pain and swelling following a trauma 15 days earlier, in which he had fallen on his left upper extremity. They concluded that the possibility of TB should be considered among young population with chronic progressive monoarticular symptoms that do not respond to conventional treatment to avoid long delay before the diagnosis and to establish the appropriate therapy [6]. Gupta et al. [7] also present similar case of 19 year old male patient.
Soman et al. [1] reported patient who had an extra articular distal radius fracture treated initially with percutaneous pinning and was treated as CRPS for the next ten months by local physician. He was eventually diagnosed with advanced tuberculosis of the wrist and a total wrist arthrodesis was performed. As precisely commented by Soman et al. [1] every case of distal radius fracture complaining of chronic pain and signs suggestive of CRPS should have tuberculosis as one of the differential diagnosis. In late diagnosed cases with severe joint destruction arthrodesis along with appropriate medical therapy is the key to achieve a painless stable joint [1].
Conclusion
Tuberculosis of wrist joint must be considered as one of the suspected diagnosis in any atypical presentation with pain and or swelling of the wrist joint as investigation facility are widely available for diagnosis of extra pulmonary tuberculosis in Indian settings.
For more articles in Open Access Journal of Case Studies please click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/jojcs/index.php



No comments:
Post a Comment