Juniper Publishers- Open Access Journal of Environmental Sciences & Natural Resources
Analysis of the Relative Contributions of Climatic Elements and Environmental Variables to Flood Disaster in Uyo, Akwa Ibom State, Nigeria
Authored by Evans UF
Abstract
The study aimed at comparing the relative contributions of climatic elements and environmental variables to flooding in Uyo, Akwa Ibom State. In achieving the aim of this study, environmental inventory was conducted to obtain data on environmental factors (number of flood channels used for dumping of refuse, number of roads without drainage channel, number of flood channels blocked by houses and other civil constructions, number of urban pavement constructed within the period and number of natural flood channels identified) within identified flood sites in Uyo from 2005-2016. In addition, the climatic elements (temperature and rainfall) data were obtained from NIMET office in Uyo for period under consideration.
The flood water discharge quantity per year, which represented the volume of flood water, was computed. Data were analyzed using multiple regression method. Results show that, rainfall and roads without good drainage channel exact significant influence on the flooding in the study area, with a significant level of 0.000 and 0.004 respectively. However, other variables (temperature, blocked flood channels by refuse and blocked flood channels by buildings) were not statistically significant in the prediction of flooding water quantity.
The study also reveals that, the highest contribution to flooding is rainfall, closely followed by the number of natural floor channels identified in the study area. It was recommended that, all roads constructed in the study area or other areas with similar topography (flat land) and geology (coastal plain sands) should be provided with good drainage channel to enable rain water drain to the nearest stream and river as this could service as a means of mitigating urban flooding. In addition, natural flood channel should be maintained as well as prohibition of the flood channels as dump sites for refuse.
Keywords: Flood; Rainfall; Climate; Environment; Inundation and Drainage
Abbreviations: FCDR: Flood Channels Used for Dumping of Refuse; RWDC: Roads without Drainage Channel; UPCD: Urban Pavement Constructed within the Period; NFCA: Natural Flood Channels Identified
Introduction
Flood is a water induced disaster that leads to temporary overflow of dry land with water and causes serious damage on lives (plants, animals, man), property, and infrastructures. During flood, water overflows into an environment that is naturally supposed to be dry thereby causing inundation and damage to the environment. Floods can also occur when the amount of water flowing from a catchment exceeds the capacity of its drains, creeks, estuaries and rivers. The oceans are the primary source for atmospheric moisture that eventually falls as precipitation to cause a flood. The atmosphere is acts as temporary reservoir and delivery system for this moisture which evaporates the moisture from the ocean surface and transports it to the continents in the form of perceptible water vapor through the large-scale motions of the general circulation of the atmosphere [1,2], observed that, flooding process begins with rainfall, and becomes enhance by environmental factors. They identified some events climatic processes capable of causing flood to include rainfall, temperature, intense convective thunderstorms, tropical storms and hurricanes, cyclones and frontal passages, and rapid snowmelt. According to [3], floods can be caused either by an excess of rainfall leading to greater surface runoff or by storm surges raising the sea level [1] opined that, when heavy rainfall occurs repeatedly over a wide area, then river or mainstream flooding becomes more probable. This situation, the main rivers of a region swells and inundates large areas, sometimes well after rainfall has ended.
In many natural systems, floods play an important role in maintaining key ecosystem functions and biodiversity. Floods link rivers with the land surrounding it, recharge groundwater systems, fill wetlands, increase the connectivity between aquatic habitats, and move both sediment and nutrients around the landscape, and into the marine environment. For many species, floods trigger breeding processes, migration, and dispersal [4]. These natural systems may be resilient to the effects of all but the largest floods. In addition, floods flood in its natural state can provide farm lands with better soil consistencies and keeps the land fertile thereby producing good harvests. Therefore, flood events can result in long-term benefits to agricultural production by recharging water resource storages, especially in drier, inland areas, and by rejuvenating soil fertility by silt deposition. Hence, rather than out right flood prevention, it is important to allow some control flow of water from Rivers into farmlands.
However, floods generally can be a bane to most people, with attendant threat to social, emotional and economic stability of affected areas. Some of the threats of flooding include displacement from homes, loss of personal valuables, fear and insecurity caused by such experience, loss of businesses patronage, stock, data and productivity. Tourism, farming and livestock can equally be affected, degrade aquatic habitats, reduce coastal production, and contaminate coastal food resources [5]. Utilities and transport infrastructure can be rendered inefficient by flood. Potable water supplies may be contaminated in a flood which has immediate health effects upon human beings and animals (Folorunsho and Awosika, 2001). Other negative effects include loss of habitat, dispersal of weed species, the release of pollutants, lower fish production, loss of wetlands function, and loss of recreational areas [4].
In addressing the issue of flooding and it associated with loses, efforts been made by some researchers showed that, the causes of flooding have been polarized into environmental Okoro et al. [5] and climatic [6]. In the light of the irreparable damage that has resulted from flooding; there is a dire need to direct urgent attention towards establishing the relative contributions of climatic elements and environmental factors as flood predictor variables in Uyo, Akwa Ibom State. This will become the driving force in ameliorating the risk of flooding in the area.
Classification of flood
Some researchers on flooding [7]; Yahaya et al. 2010; Adebayo et al. 2011; [3] have classified floods into three main forms - coastal flooding, river flooding and urban flooding.Coastal flooding occurs in the low-lying belt of mangrove and fresh water swamps along the coast, river flooding occurs in the flood plains of the larger rivers, while short-lived flash floods are associated with rivers in the inland areas and sudden heavy rains that change into a destructive torrent within a short period. Periodic floods can occur in Rivers, forming a surrounding region known as flood plain.
According to [8], flood resulting from rivers has relatively high flow, which overtakes the natural channels provided for run-off as well as a high stream which overtops its natural or artificial banks. Urban flooding on the other hand occurs in towns, on flat or lowlying terrain especially where little or no provision made for surface drainage or where existing drainage has been blocked with municipal waste, refuses and eroded soil sediments. Rainfall is the most important factor in creating a flood; however, there are many other contributing factors such as catchment size, shape and land use. Flood is most likely to occur in most wetland/coastal areas of the world. This is because of the general rise in sea level globally, due to global warming as well as the saturated nature of the wetlands in the Riverine areas. The urban flooding type is what is experienced in Uyo.
Adeleye et al. 2011 [9] noted that, torrential rains made rivers to overflow their banks and caused mud houses to collapse and also washed away livestock. In some places and cases, flooding has damaged bridges and caused overflow of dams, submergence of buildings, displacement of people from their homes, loss of people's valuables and loss of life. The economy of a place can also be severely affected as most businesses may lose stock due to flooding. However, urban areas especially in developing countries experience various types of flood disaster in most of the rainy seasons. Rainy Season floods are produced by heavy rainfall that wets ground which penetrates into lands which were previously dry. The destructive effects of flood in urban areas have been discussed extensively by researcher [8]. Although floods can happen at any time of the year, but the Uyo Local Government Area has typical seasonal patterns of flooding, which is associated with the rainy season.
The flooding in Uyo can be attributed to urbanization, which resulted to serious modification of the natural environment in an attempt for man to achieve certain level of comfort. However, the need to compare the contributions of climatic element and the environmental variables to flooding to ascertain their relative contributions to urban flooding has largely been ignored in relevant literature especially when it comes to the study area. When rain falls, some of the rain water is captured by soil and vegetation, and the remainder enters waterways and flow into streams, creeks, lakes, and rivers. River characteristics such as size and shape, the vegetation in and around the river, and the presence of structures in and adjacent to the waterway all affect the level of water in the waterway leading to a much higher variability of the amount of water flowing through our waterways.
Study Area
Geographically, the study area is located between Latitudes 4°32'N and 5° 33'N and Longitudes 7 ° 25'E and 8°25'E. Uyo is a table land situated in the tropical rainforest, and drained by streams and Rivers. It is one of the rapid growing state capitals ' in Nigeria, thereby attracting much improvement on available r land. The level of urbanization in Uyo has greatly modified the natural environments in other to satisfy the needs of the seemingly increasing population. Urbanization is not without its attendant challenges especially in the areas of waste disposal and sustainable development.
Uyo is situated on a flood plain and is extremely vulnerable ' to flooding. It is observed that flooding in Uyo seems to happen ; every year. For instance, Uyo witnessed flood in 2010, 2011, | 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015, 2016 and 2017. However, the most 1 severe flood struck in Uyo was that of 17th October 2013, where : 100s of homes in the city were inundated. Therefore, flooding is one of the major environmental challenges pervasive in Uyo, Akwa Ibom State, which some of the hot spots are Atan Offot, Atiku Abubakar, Abak Road, Aka Itiam, Urua Ekpa, Aka/Etinan n(By C- Division) and the State Secretariat Complex area.
Methodology
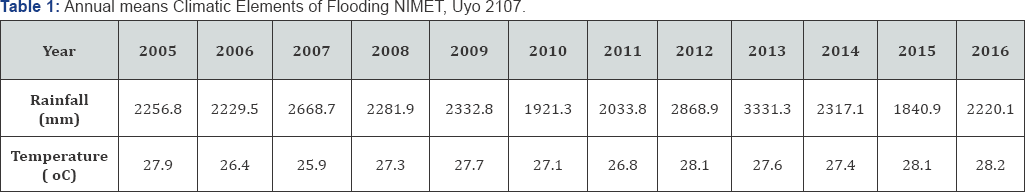
The approach to this was the design of flood inventory data sheet, which was prepared by the researchers, and used to elicit information on the environment condition of the study area. The items enumerated on the data sheet were: number of flood channels used for dumping of refuse (FCDR); number of roads without drainage channel (RWDC); number of flood channels blocked by houses and other civil constructions (FCBH); number of urban pavement constructed within the period (UPCD) and number of natural flood channels identified (NFCA). The study was complemented by ten years climatic data temperature and rainfall (Table 3.1), obtained from Nigerian Meteorological (NIMET) Agency Synoptic station in Uyo. While the Khosla's formula was used to estimate flood discharge quantity (q) in the study area given as
q = p - kTm
Where p is a constant given by 0.4813 (Ezenwaji et al. 2013)., Tm is the mean yearly temperature in 0C (Table 1).
Results and Discussion
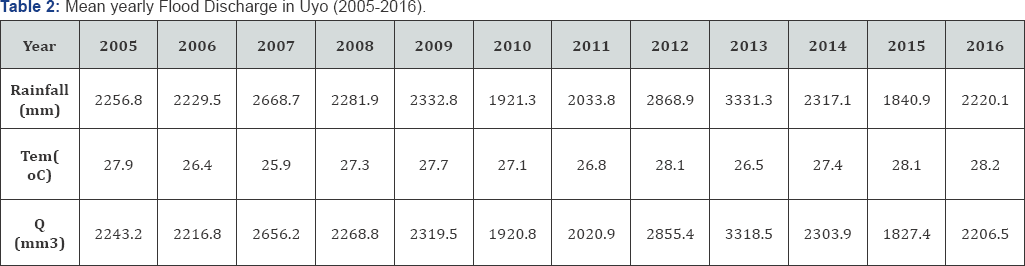
The result of the yearly flood discharge and climatic elements in the study area are contained in table 2. The result shows that the highest quantity of rainwater was in 2013, while the least was recorded in 2015 (Table 2).
The relationship between Climatic elements, Environmental Factors and flooding discharge in Uyo
In order to establish the relationship between Climatic elements, environmental factors and flood discharge, the multiple regression analysis was carried out using the SPSS software. The result is shows that rainfall and roads without good drainage channel exact significant influence on the flooding in the study area, with a significant level of 0.000 and 0.004 respectively. The result also suggest that, other variables (temperature, blocked flood channels by refuse and blocked flood channels by buildings) are not statistically significant in the prediction of flooding in Uyo. A strong correlation (1.00) of flooding and rainfall was obtained, while the correlation of flooding with temperature gave a negative value of -0.304. All the environmental factors produced weak correlation (0.0120.200) with flooding in the study area (Table 3).
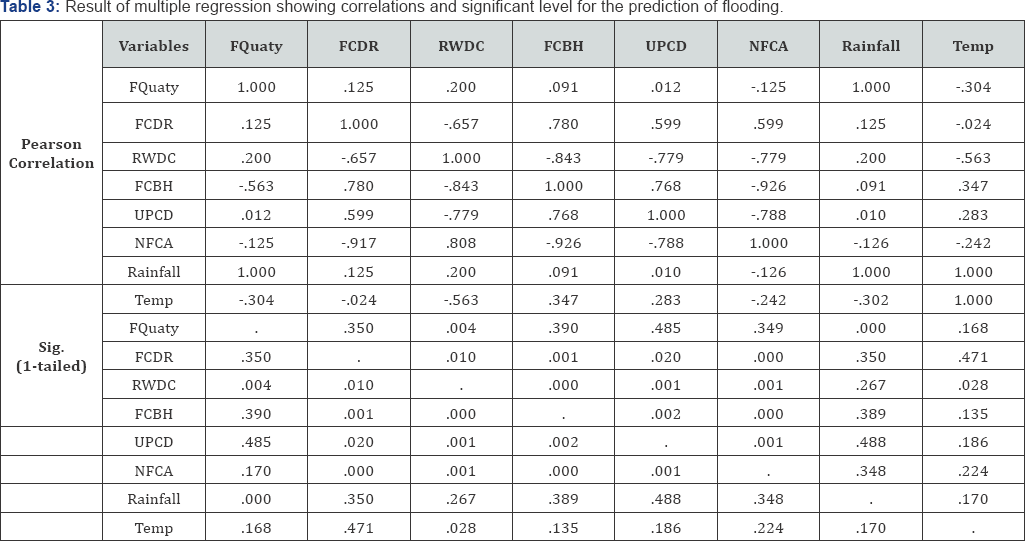
This result gives the true condition of flooding in the study area. It implies that flooding in the study area is significantly influenced by rainfall (climatic element). However, the environmental conditions can only enhance the severity of the damage due to flooding. The is in agreement with [5], they observed that flood is basically caused by heavy down pour, while the environmental conditions determined the extent to the discharge water is retained, as well as the damaged caused by flood. In addition [7] explained that, if the natural flood channels are maintain, the hazard caused by flooding could be kept at minimal since the volume of flood water at a time and in a given location (inter land) will be low.
Strengths of causation by climatic element and environmental factors to flooding in Uyo
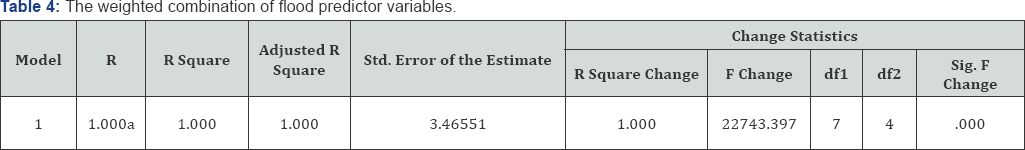
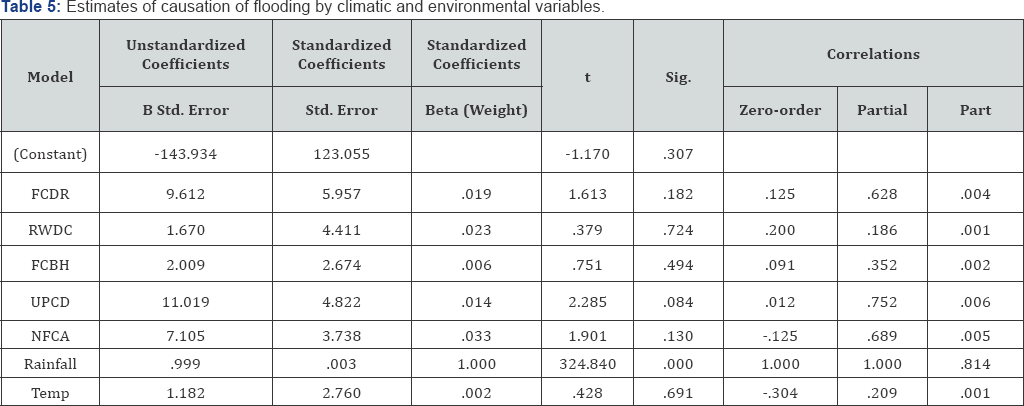
Table 4 is the combined weighted strength of the predictor variables used for the study. The values of R square and adjusted R indicate that, the combined weight of the predictor variables can explain 100% of the variance in flooding in Uyo. However,Table 5 shows the estimate of flood causation by each variable. The Beta (weight) expresses the estimate at which the predictor variables contribute to flooding in the study area [9-13].
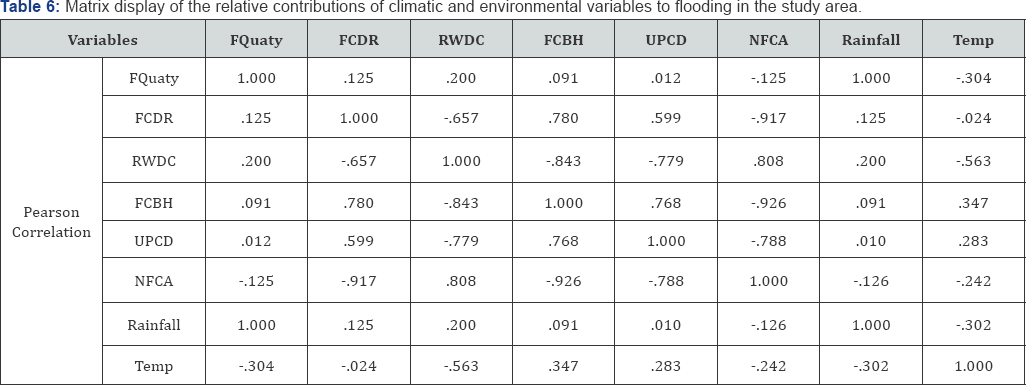
The highest contribution is the rainfall, followed by number of natural floor channels identified in the study area. Number of roads without drainage channel showed the least contribution (0.003) to flooding (Table 6) is the matrix display of the relative contributions of climatic and environmental variables to flooding in the study area. It is obvious that, climatic elements are the major contributors to flooding in the study area. This is aided by the roads without good drainage channels and closely followed by flood channels used for dumping of refuse (Table 4).
Conclusion
The contributions of climatic elements (temperature and rainfall) and environmental factor to flooding in Uyo have been investigated using 12 years data collected from NIMET, Uyo and a structured inventory data sheet was to collect information on the environmental factors in the study area. The contributions to flooding in Uyo by environmental factors were noticed to be insignificant except for roads without drainage channel (RWDC). For instance the following level of significant was obtained for the five environmental factors used for the study, number of flood channels used for dumping of refuse (FCDR) 0.350, number of roads without drainage channel (RWDC) 0.004, number of flood channels blocked by houses and other civil constructions (FCBH) 0.390, number of urban pavement constructed within the period (UPCD) 0.485 and number of natural flood channels identified (NFCA) 0.349. A significant level of contribution for climatic elements was achieved rainfall 0.000. However, the contribution to flooding in Uyo by temperature was seen to be insignificant 0.168.
The estimated strength by which the individual variable contributes to flooding according to the research is FCDR 0.125, RWDC 0.200, FCBH 0.091, UPCD 0.012, NFCA -0.125, Rainfall 1.000 and Temp -0.304. These by implication, means that, rainfall is the major cause of flooding in Uyo, which may not be the case in coastal communities where there is possibility of major flooding informed by sea level rise. In addition, road without drainage channel (RWDC) is observed to highest estimated strength among the identified environmental factors. Therefore, all roads constructed in the study area or other areas with similar topography (flat land) should be provided with good drainage channel to enable rain water drain to the nearest stream as this could service a means of mitigating urban flooding. In addition, natural flood channel should be maintained as well as prohibition of the flood channels as dump sites for refuse.



No comments:
Post a Comment