Juniper Publishers- Open Access Journal of Case Studies
Low Serum Ferritin Probably Independent Risk Factor for Gallstones Formation - Case Study
Authored by Walaa Fikry Elbossaty
Abstract
Iron deficiency anemia is one of the most popular types of anemia in the Middle East, which is characterized by a severe deficiency in the proportion of hemoglobin and ferritin. The prevalence of iron deficiency anemia in women increases more than men, as they are more likely to lose blood. It was found that there is a relationship between the rate of iron deficiency and the development of gallstones. This is due to many vital processes in which iron contributes as a catalyst for some vital enzymes or influences rates of liver enzymes that have an effective role in the process of stone formation.
In this study we tried to study the relationship between iron deficiency anemia and the formation of gallstones, in addition to the use of ferritin as a preliminary indicator to predict the possibility of forming gallstones and then take the necessary preventive measures. So, ferritin is independent risk factor for gallstones formation.
Keywords:Iron deficiency anemia; IDA; GS; NOS; Liver enzymes
Background
The gallstones (GB) are one of the most common diseases that affect the digestive system and cause many health problems. Women are more likely to be gallstones; in addition to that it may appear in men. Stones may appear as a large stone or a group of small stones that group together in groups. Stones consist of mixture of cholesterol, bilirubin with, or without calcium [1].
Researches indicated that there is relation between gallstones formation and iron deficiency anemia (IDA) [2].
Iron deficiency anemia result from the negative balance between iron requirements and iron intake. This decrease may be due to malabsorption, malnutrition, excessive blood loss, inflammation in digestive system. Here we present patient with iron deficient anemia then developed gallstones [3].
Objective
The aim of the study was to determine the relationship between iron deficiency and the formation of gallstones with the use of ferritin as an indicator for the determination of iron deficiency anemia.
Case Report
18 - Years old - gentle woman was diagnosed with iron deficiency anemia in 2019. She presented to hospital in March 2019 with 4-week history of left upper quadrant abdominal pain associated with anorexia and easy fatigability. Physical examination was positive for pallor. Lab tests on presentation showed: white blood cells (WBCs) of 10.43 with monocytosis.
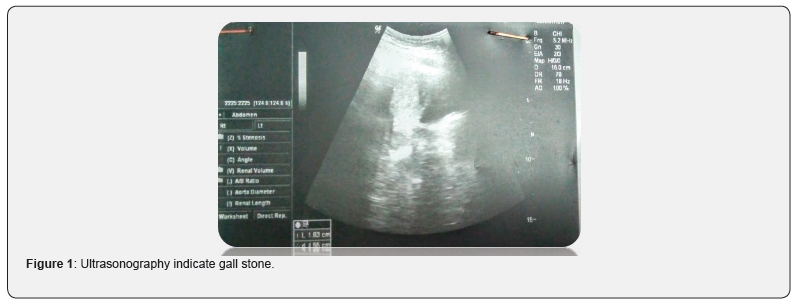
Hemoglobin (Hb) was 6.9g/dL, with mean corpuscular volume (MCV) of 54, RDWc 21.1 and platelets of 187.S. ferritin level is 2.3ng/ml. Renal and liver function tests were within normal limits. She is suffering from cholelithiasis confirmed by ultrasonography (Figure 1).
Discussion
There are many factors that help in the formation of gallstones, including: the concentration of bilirubin, the superior saturation of the bile in the bile ducts, the change in the degree of pH, some electrolytic materials such as copper, zinc, iron, and calcium play an important role in the formation of stones, in addition to iron deficiency anemia [4].
Iron deficiency anemia plays an important role in changing liver enzymes and thus increases the rate of super saturation for the bile, and thus helps in the formation of gallstones in addition to that iron acts as a catalyst in relation to nitric oxide synthetases (NOS) and this helps in the formation of nitric oxide, which has an effective role in improving the function of the gallbladder and its relaxing [5].
Conclusion
It was found that there is a relationship between the iron deficiency rate and the rate of formation of gallstones. Ferritin plays an effective predictor in identifying iron deficiency anemia. Then ferritin can be used as a diagnostic device to predict the presence of gallstones.
To know more about Juniper Publishers please click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/manuscript-guidelines.php
For more articles in Open Access Journal of Case Studies please click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/jojcs/index.php



No comments:
Post a Comment